The Ultimate Guide to Tri-Potassium Phosphate: Properties, Uses, and Benefits
Unlocking the Potential: An Ultimate Guide about Tri-Potassium Phosphate

- August 11, 2023
- By Akshita Patel
Tri Potassium Phosphate (TKP), also known as potassium phosphate tribasic, is a chemical compound with a significant presence in various industries due to its versatile properties and wide-ranging applications. The unique molecular arrangement grants TKP its distinctive characteristics, making it a valuable ingredient in multiple sectors. Tri Potassium Phosphate is a white crystalline powder that is readily soluble in water, leading to its extensive use in both aqueous and solid formulations. Its chemical structure contributes to its role as a source of potassium and phosphate ions, which are essential nutrients for plant growth and various biochemical processes.
Chemical Structure and Formula
TKP’s chemical formula, K3PO4, provides insights into its composition. The arrangement of these atoms defines TKP’s properties and capacity to release potassium and phosphate ions when dissolved in water or other solvents. This property, in turn, influences its effectiveness in various applications.
Physical Properties of TKP
- Appearance: Tri Potassium Phosphate typically presents itself as a white crystalline powder. This form allows for easy handling and incorporation into different formulations.
- Solubility: TKP is highly soluble in water, forming an alkaline solution. This solubility contributes to its role in pH regulation and utilization in various liquid-based applications.
- Hygroscopic Nature: The compound’s hygroscopicity indicates its tendency to absorb environmental moisture. This characteristic makes TKP suitable for applications requiring humidity control and moisture management.
Availability and Forms of TKP in the Market
Annexe Chem is a leading manufacturer of Tri Potassium Phosphate based in India, dealing with meticulously formulated to meet the highest industry standards, ensuring exceptional quality and performance. Tri Potassium Phosphate is commercially available in several forms to cater to specific industry needs:
- Anhydrous Form: This form contains no water molecules and is often used in applications where precise dosing and water content control are crucial. It’s commonly employed in food and beverage processing, as well as in various industrial processes.
- Hydrated Forms: TKP is also available in various hydrated forms, including dihydrate (K3PO4·2H2O) and trihydrate (K3PO4·3H2O). These forms can offer advantages in specific applications, such as in the agricultural sector, where controlled release of nutrients is desired.
- Custom Blends: In some instances, TKP might be blended with other compounds or additives to achieve desired properties or performance characteristics. These custom blends can be tailored to suit the needs of specific industries or processes.
Usage of Tri Potassium Phosphate
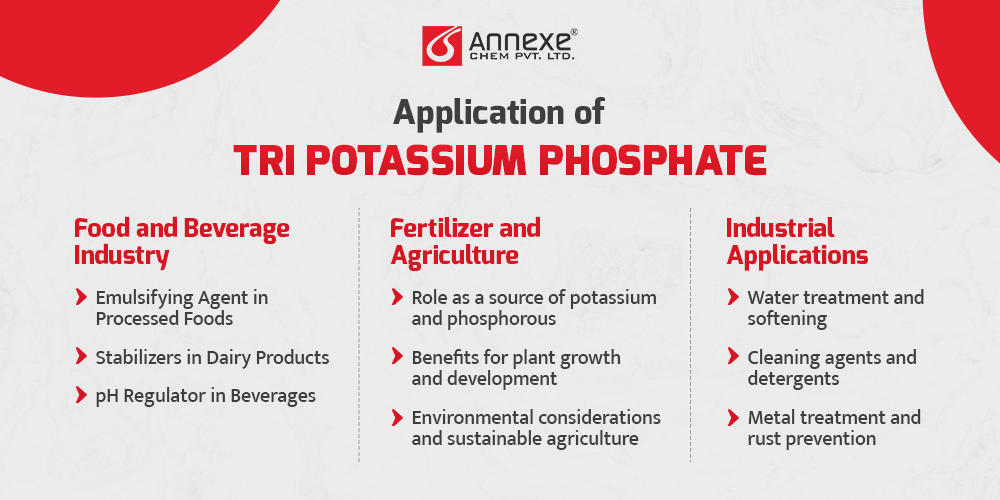
Food and Beverage Industry
- Emulsifying Agent in Processed Foods: TKP functions as an emulsifier, facilitating the blending of typically immiscible ingredients in processed foods. This role ensures the even distribution of fats, oils, and water, resulting in improved texture, consistency, and stability. Salad dressings, baked goods, and sauces are examples of products benefitting from TKP’s emulsifying properties.
- Stabilizer in Dairy Products: In dairy items like ice cream, yogurt, and cheese, TKP acts as a stabilizer. It prevents crystallization and separation, enhancing the overall creaminess and shelf life of these products.
- pH Regulator in Beverages: TKP’s alkaline properties make it an effective pH regulator in beverages. It helps maintain the desired acidity levels and stabilizes flavors, ensuring consistent taste profiles in products like soft drinks, fruit juices, and energy drinks.
Fertilizer and Agriculture
- Role as a Source of Potassium and Phosphorus: TKP’s contribution to agriculture is primarily as a source of essential nutrients—potassium and phosphorus. These nutrients are crucial for plant growth, root development, and overall metabolic functions. Incorporating TKP into fertilizers enhances soil fertility and crop yield.
- Benefits for Plant Growth and Development: The potassium and phosphorus derived from TKP play a pivotal role in enhancing plant resilience to stress, improving flower and fruit formation, and bolstering disease resistance. This leads to healthier, more robust crops.
- Environmental Considerations and Sustainable Agriculture: TKP’s utilization in agriculture aligns with sustainable practices. By optimizing nutrient uptake and reducing excessive fertilizer use, TKP promotes efficient resource utilization and minimizes environmental impact.
Industrial Applications
- Water Treatment and Softening: In water treatment processes, TKP assists in water softening by binding to hardness ions such as calcium and magnesium, preventing scale formation in pipelines and appliances. This property contributes to improved water quality and extended equipment lifespan.
- Cleaning Agents and Detergents: TKP’s ability to stabilize formulations makes it an asset in cleaning agents and detergents. It helps maintain the consistency of these products and enhances their performance by aiding in soil suspension and removal.
- Metal Treatment and Rust Prevention: TKP’s hygroscopic nature renders it useful in metal treatment to prevent rust and corrosion. When incorporated into coatings or inhibitors, it forms a protective barrier that shields metal surfaces from moisture-induced degradation.
Tri Potassium Phosphate’s diverse applications across these industries underscore its significance in enhancing product quality, supporting agriculture, and contributing to various industrial processes. As we explore further, we will examine the safety aspects, proper handling practices, and future trends associated with TKP’s utilization.
Safety and Handling
Ensuring the safe handling of Tri Potassium Phosphate (TKP) is paramount across its diverse applications. A comprehensive understanding of potential risks, storage practices, and regulatory guidelines is crucial for minimizing hazards and promoting responsible use. While TKP is generally considered safe when handled properly, it’s essential to be aware of potential hazards:
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Direct contact with TKP can lead to skin and eye irritation. Personal protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn during handling.
- Inhalation Risks: Inhaling TKP dust may cause respiratory irritation. Adequate ventilation and respiratory protection should be employed when working with the compound in powdered form.
- Ingestion Dangers: Ingesting TKP can result in digestive discomfort. It is crucial to prevent accidental ingestion and maintain proper hygiene practices.
Proper Storage and Handling Practices
Adhering to proper storage and handling practices ensures both personal safety and product integrity:
- Storage: TKP should be stored in dry, well-ventilated areas, away from incompatible substances such as acids and strong oxidizers. Keep containers tightly closed to prevent moisture absorption.
- Handling: Avoid generating dust by minimizing handling and utilizing closed systems whenever possible. If dust is generated, wear appropriate protective equipment and work in a controlled environment.
- Spill and Leak Management: In case of spills or leaks, clean up promptly using appropriate methods to prevent environmental contamination.
Regulatory Guidelines and Safety Measures
Familiarizing yourself with relevant regulatory guidelines and safety measures is essential:
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Obtain and review the SDS for TKP from your supplier. This document provides essential information on hazards, safe handling practices, and emergency procedures.
- Labeling and Warning: Ensure containers are properly labeled with hazard symbols, precautionary statements, and handling instructions.
- Training: Educate personnel about the proper handling procedures, potential hazards, and emergency response protocols.
How to Choose and Purchase TKP
Choosing the right TKP and sourcing it from reliable suppliers is crucial for achieving desired results in various applications.
Evaluating Purity and Quality
- Purity: Higher purity TKP is usually preferred, especially for applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Ensure the product meets industry standards.
- Certifications: Look for suppliers that adhere to relevant quality standards and certifications, such as ISO or food-grade certifications.
Selecting the Appropriate Form for Specific Applications
- Anhydrous vs. Hydrated: Choose the form that aligns with your application’s requirements for water content and release characteristics.
- Custom Blends: If needed, explore suppliers offering custom blends that incorporate TKP with other additives for specific functionalities.
Reliable Suppliers and Sourcing Options
- Supplier Reputation: Research suppliers’ reputations, customer reviews, and industry experience.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Consider suppliers with consistent product availability and reliable delivery timelines.
- Technical Support: Opt for suppliers that offer technical support and assistance in selecting the right TKP for your applications.

Future Trends and Developments
The evolution of Tri Potassium Phosphate continues with ongoing research and innovation, aiming to expand its applications while aligning with sustainable practices.
Research and Innovation in TKP Applications
- Advanced Formulations: Researchers are exploring novel formulations that harness TKP’s properties for new applications in fields like pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Functionalized TKP: Modified versions of TKP are being developed to enhance its performance in specific applications, such as controlled-release fertilizers.
Sustainable Production Methods and Eco-Friendly Alternatives
- Green Chemistry: Efforts are being made to develop eco-friendly production methods that minimize waste and environmental impact.
- Alternative Sources: Research into alternative sources of potassium and phosphorus could provide sustainable alternatives to traditional TKP.
Emerging Industries Where TKP Might Play a Significant Role
- Advanced Materials: TKP’s properties could find applications in advanced materials, such as ceramics and coatings, for improved performance and durability.
- Biotechnology: As biotechnology advances, TKP’s role in nutrient delivery systems and controlled-release technologies could become more prominent.
Whether you’re in the food industry, agriculture, or seeking solutions for industrial processes, Tri Potassium Phosphate offers a world of possibilities. Explore its diverse applications, enhance your products, and contribute to sustainable practices. Embrace innovation and make TKP a cornerstone of your success. Start your journey today with Annexe Chem Pvt. Ltd.

Akshita Patel
As an advocate for sustainability, Akshita is committed to driving positive change within the chemical industry. She actively seeks out environmentally friendly solutions and promotes the adoption of sustainable practices. Akshita believes that a balance between economic growth and ecological responsibility is crucial for the industry's long-term success. She is dedicated to finding innovative ways to minimize environmental impact while maximizing efficiency and profitability.
Related Blogs

- September 12, 2023
- By Akshita Patel
From Soil to Skin: Urea’s Diverse.
In the intricate tapestry of chemistry's contributions to human progress, few compounds have woven themselves into.

- January 8, 2024
- By Akshita Patel
Calcium Carbonate: Your Go-to Guide
Calcium carbonate is a chemical composite with the formula CaCO3. It's a white powder or colorless.