Di-ammonium Hydrogen Phosphate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Essential Food and Industrial Compound - Annexe Chem Pvt Ltd
Di-ammonium Hydrogen Phosphate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Essential Food and Industrial Compound

- April 26, 2024
- By Akshita Patel
Picture this: A farmer diligently tending to rows of crops, ensuring they receive the necessary nutrients for robust growth. Among the array of tools at their disposal, DAP stands out as a stalwart ally, delivering essential nutrients to the soil and the plants themselves. But what exactly is DAP, and why does it hold such sway in the agricultural realm?
In this exploration, we delve deep into Di Ammonium Hydrogen Phosphate, uncovering its chemical composition, myriad applications, environmental implications, and the evolving landscape of its usage. From its humble beginnings in the laboratory to its pivotal role in global agriculture, join us on a journey to understand the power and potential of DAP.
What is Di-ammonium Hydrogen Phosphate?
Di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate (DAP) is a versatile inorganic compound widely used in various industries, notably food production. Its chemical formula, (NH4)2HPO4, reflects its composition of two ammonium ions, one hydrogen ion, and one phosphate ion.
Chemical Formula and Structure
The chemical structure of DAP consists of a central phosphate ion (PO4³⁻) surrounded by two ammonium ions (NH4⁺) and one hydrogen ion (H⁺). This arrangement results in a crystalline solid with a strong ionic bond character.
The ammonium ions in DAP contribute two nitrogen atoms, while the phosphate ion provides one phosphorus atom. This unique combination makes DAP an excellent source of nitrogen and phosphorus, two essential nutrients required for plant growth and development.
Physical Properties
- Appearance: DAP is a white, crystalline solid with a granular or powdery texture. It is odorless and has a slightly saline taste.
- Solubility: One of the key properties that make DAP attractive for various applications is its high solubility in water. At room temperature, DAP has a solubility of approximately 588 grams per liter of water. This solubility ensures efficient nutrient delivery in agricultural applications and facilitates its use in various industrial processes.
- Non-hygroscopicity: Unlike other fertilizers and salts, DAP is non-hygroscopic, meaning it does not readily absorb moisture from the air. This property enhances its handling, storage, and transportation, reducing the risk of caking or clumping.
- Thermal Stability: DAP exhibits good thermal stability, making it suitable for processes involving elevated temperatures, such as ceramics or flame retardant production.
- pH: DAP exhibits a slightly acidic pH in aqueous solutions, typically ranging from 5.5 to 6.5. This property can be beneficial in certain applications where pH control is crucial, such as in the food industry or specific agricultural practices.
These physical and chemical properties of di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate contribute to its widespread utility and make it a valuable compound in various industrial sectors.
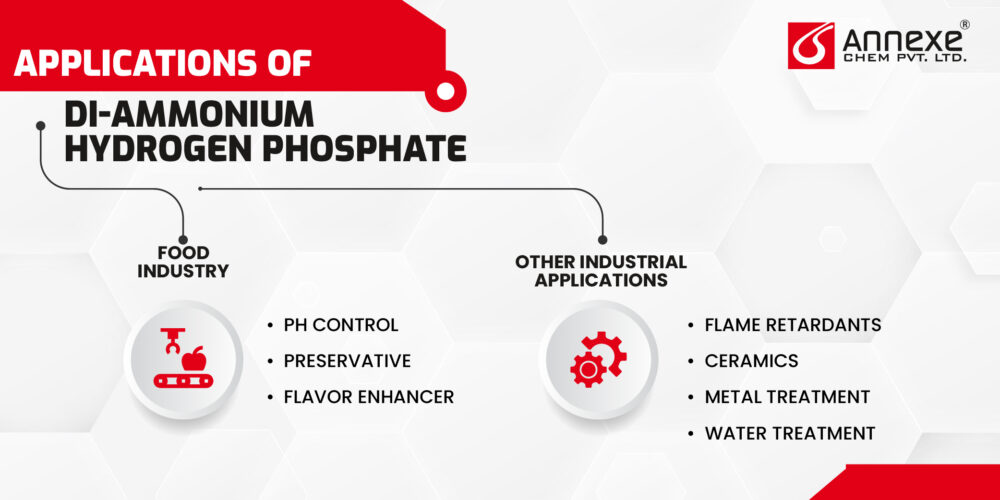
Applications of Di-Ammonium Hydrogen Phosphate
Di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate (DAP) is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications across various industries, primarily due to its unique chemical composition and properties.
Food Industry
Use as a Leavening Agent In the food industry, DAP is commonly used as a leavening agent, particularly in baked goods such as crackers, cookies, and biscuits. When heated, DAP releases ammonia gas, which causes the dough or batter to rise and create a light, airy texture. Other Food-Grade Applications Beyond its use as a leavening agent, DAP finds applications in various other food-related processes:
- pH control: Due to its slightly acidic nature, DAP can be used as a pH buffer in certain food products, ensuring optimal acidity levels for taste, preservation, and functionality.
- Preservative: The ammonium ions present in DAP can act as preservatives, inhibiting the growth of certain microorganisms and extending the shelf life of food products.
- Flavor enhancer: In some cases, DAP can be used as a flavor enhancer, particularly in savory or salty foods, due to its mild saline taste.
Other Industrial Applications
The versatility of di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate extends beyond the fertilizer and food industries. It finds applications in several other sectors, including:
- Flame Retardants: DAP is used as a flame retardant additive in various materials, such as plastics, textiles, and insulation materials, due to its ability to release ammonia gas and water vapor when heated, reducing the risk of combustion.
- Ceramics: DAP is employed as a binder and flux agent, facilitating the formation and sintering of ceramic materials at lower temperatures.
- Metal Treatment: DAP can be used in metal treatment processes, such as pickling, to remove surface oxides and prepare metal surfaces for further processing or coating.
- Water Treatment: The ability of DAP to control pH and act as a nutrient source makes it useful in certain water treatment applications, such as aquaculture or wastewater treatment systems.
These diverse applications of di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate highlight its significance and versatility across various sectors, contributing to agricultural productivity, food quality, and industrial processes.
Future Prospects & Trends Of Di-Ammonium Hydrogen Phosphate:
As the world continues to evolve, the demand for versatile and efficient compounds like di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate (DAP) is expected to rise. The future holds promising prospects and trends for this remarkable chemical, driven by technological advancements, emerging applications, and market growth.
Advancements in Production Methods
The production of DAP has traditionally involved energy-intensive processes and the consumption of non-renewable resources. However, researchers and manufacturers are actively exploring more sustainable and efficient production methods to meet the growing demand while minimizing environmental impact. One promising area of research is the development of alternative production routes that utilize renewable resources or waste materials as feedstocks. For instance, some studies have explored the possibility of producing DAP from agricultural waste streams, such as animal manure or crop residues, which could reduce the environmental footprint and contribute to the circular economy. Additionally, advances in process optimization and integration of innovative technologies, such as membrane separation or catalytic processes, could lead to more efficient and cost-effective DAP production methods, further enhancing its accessibility and affordability.
Emerging Applications
While DAP has established its importance in industries like agriculture, food, and ceramics, ongoing research is unveiling new and exciting applications for this versatile compound:
- Energy Storage: DAP’s ability to release ammonia gas and water vapor when heated has sparked interest in its potential use as a hydrogen carrier for energy storage and transportation applications.
- Environmental Remediation: The high nutrient content of DAP makes it a promising candidate for environmental remediation techniques, such as bioremediation or phytoremediation, where it can promote the growth of microorganisms or plants capable of breaking down or immobilizing pollutants.
- Biomedical Applications: Preliminary research has explored the potential use of DAP in biomedical applications, such as drug delivery systems or tissue engineering scaffolds, due to its biocompatibility and ability to control pH and nutrient release.
As research continues to uncover new applications, the versatility of DAP is expected to expand, opening up new avenues for its utilization across various sectors. With its diverse applications, ongoing technological advancements, and favorable market conditions, di-ammonium hydrogen phosphate is poised to play an increasingly significant role in different sectors shaping a more sustainable and efficient future.
At the forefront of DAP production stands Annexe Chem Pvt Ltd, a leading manufacturer and exporter based in Vadodara, India. With a commitment to quality and sustainability, Annexe Chem continues to drive advancements in DAP technology, ensuring its efficacy and environmental responsibility. At Annexe Chem, sustainability is at the core of everything we do. We recognize the importance of responsible manufacturing practices and environmental stewardship in safeguarding our planet for future generations. Through our state-of-the-art facilities and stringent quality control measures, we strive to produce DAP of the highest standards while minimizing our environmental footprint.
Together, let us continue to cultivate success, enriching lives and nurturing growth every step of the way.

Akshita Patel
As an advocate for sustainability, Akshita is committed to driving positive change within the chemical industry. She actively seeks out environmentally friendly solutions and promotes the adoption of sustainable practices. Akshita believes that a balance between economic growth and ecological responsibility is crucial for the industry's long-term success. She is dedicated to finding innovative ways to minimize environmental impact while maximizing efficiency and profitability.
Related Blogs

- October 30, 2024
- By Akshita Patel
The Versatile Uses of Zinc Sulphate:.
From the food you eat to the products you use daily, zinc plays an unsung yet.

- August 20, 2024
- By Akshita Patel
Exploring the Applications and Benefits of.
When it comes to versatile chemical compounds, Tri-Sodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate (TSP Dodecahydrate) stands out as a.