Understanding Calcium Hydroxide: Properties, Uses, and Safety - Annexe Chem Pvt Ltd
Understanding Calcium Hydroxide: Properties, Uses, and Safety

- June 18, 2024
- By Akshita Patel
Calcium Hydroxide, often known by its common names slaked lime or hydrated lime, is a versatile chemical compound with a wide range of applications. From its critical role in construction and water treatment to its use in the food industry and medical field, Calcium Hydroxide is an unsung hero in many essential processes.
What is Calcium Hydroxide?
Calcium Hydroxide, with the chemical formula Ca(OH)₂, is an inorganic compound that is widely utilized in various industries due to its reactive properties. This compound is created through the process of combining calcium oxide (quicklime) with water, resulting in an exothermic reaction that produces calcium hydroxide and heat.
Definition and Chemical Composition
Calcium Hydroxide is defined as a white, powdery substance composed of calcium, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Its chemical composition is represented by the formula Ca(OH)₂, indicating that each molecule contains one calcium atom bonded to two hydroxide groups. This structure makes it a strong base, capable of neutralizing acids and participating in various chemical reactions.
Common Names
Calcium Hydroxide is known by several common names, reflecting its different uses and forms:
- Slaked Lime: This name emphasizes the hydration process that converts calcium oxide to calcium hydroxide.
- Hydrated Lime: A term used to denote the water content in the compound.
- Pickling Lime: Refers to its use in the food industry, particularly in the pickling process.
- Builders’ Lime: Commonly used in construction and masonry.
Natural Occurrence
In nature, Calcium Hydroxide is found in its mineral form known as portlandite. However, it is more commonly produced synthetically for industrial and commercial applications. The natural occurrence of calcium hydroxide in portlandite is relatively rare, and it is usually encountered in association with volcanic and metamorphic rocks. This mineral can be found in regions with significant geological activity, where high temperatures and pressures facilitate its formation.
In summary, Calcium Hydroxide is a versatile and essential compound with a straightforward yet powerful chemical composition. Its various names and forms reflect its widespread utility across different sectors, and while it does occur naturally, it is predominantly manufactured to meet the demands of modern industry.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Calcium Hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂, possesses a range of physical and chemical properties that make it a valuable substance in various applications. Understanding these properties is essential for effectively utilizing and handling this compound.
Appearance and Physical State
Calcium Hydroxide typically appears as a white, odorless powder or crystalline substance. In its solid state, it can be fine and soft to the touch, or it may form larger crystalline aggregates. When mixed with water, it forms a slurry or a viscous paste, which is often referred to as lime putty.
Solubility and pH
Calcium Hydroxide is sparingly soluble in water. At 20°C, about 1.73 grams of Calcium Hydroxide dissolve in one liter of water, forming a solution known as limewater. This solution is mildly alkaline, with a high pH value typically around 12.4. This high pH indicates that Calcium Hydroxide is a strong base, capable of neutralizing acids effectively.
Stability and Storage Conditions
Calcium Hydroxide is generally stable under normal conditions. However, it must be stored properly to maintain its reactivity and prevent it from degrading. Key storage conditions include:
- Dry Environment: Calcium Hydroxide should be kept in a dry place to avoid reaction with moisture from the air, which can lead to the formation of calcium carbonate.
- Airtight Containers: To prevent absorption of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, it is best stored in airtight containers.
- Cool and Shaded Area: Storing it in a cool and shaded area helps to maintain its stability and extend its shelf life.
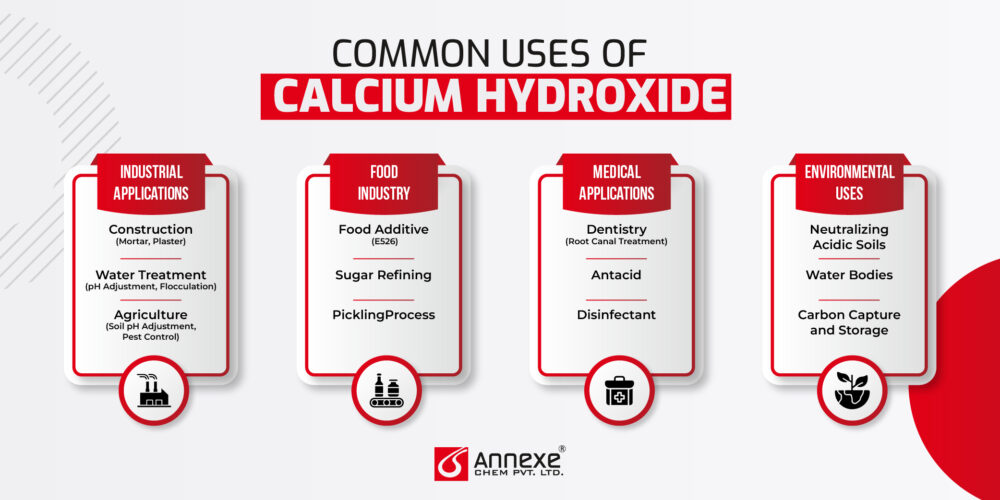
Common Uses of Calcium Hydroxide
Industrial Applications
- Construction (Mortar, Plaster): Calcium Hydroxide is a fundamental component in the construction industry. It is used to produce mortar and plaster, materials critical for masonry and finishing works. When mixed with sand and water, it forms a paste that hardens over time through a process known as carbonation, where it reacts with atmospheric carbon dioxide to form calcium carbonate. This reaction not only provides structural strength but also enhances the durability and longevity of the constructed elements.
- Water Treatment (pH Adjustment, Flocculation): In water treatment, Calcium Hydroxide is employed to adjust the pH levels of acidic water, bringing it to a neutral or slightly alkaline state. This pH adjustment is essential for protecting pipes and other infrastructure from corrosion. Additionally, Calcium Hydroxide facilitates flocculation, where it helps in aggregating suspended particles into larger clusters that can be easily removed, thus improving water clarity and quality.
- Agriculture (Soil pH Adjustment, Pest Control): Calcium Hydroxide plays a vital role in agriculture by neutralizing acidic soils, making them more conducive for crop growth. By adjusting soil pH, it enhances nutrient availability and improves soil structure. Moreover, it is used as a pesticide to control various pests and diseases, thanks to its alkaline nature, which creates an inhospitable environment for many harmful organisms.
Food Industry
- Food Additive (E526): Calcium Hydroxide is approved as a food additive (E526) and is used to fortify foods with calcium, improve texture, and regulate acidity.
- Sugar Refining: In the sugar industry, Calcium Hydroxide is used to purify sugarcane juice or beet juice by removing impurities. This process, known as liming, results in high-quality, refined sugar.
- Pickling Process: In pickling, Calcium Hydroxide is used to maintain the firmness of vegetables and fruits. It helps preserve their texture and prevents them from becoming overly soft during the pickling process.
Medical Applications
- Dentistry (Root Canal Treatment): In dentistry, Calcium Hydroxide is used in root canal treatments to disinfect root canals and promote healing. It helps eliminate bacteria and prevent reinfection.
- Antacid: Calcium Hydroxide is sometimes used in antacid formulations to neutralize stomach acid and relieve symptoms of indigestion and heartburn.
- Disinfectant: It also serves as a disinfectant in various medical and hygiene applications, helping to eliminate harmful pathogens.
Environmental Uses
- Neutralizing Acidic Soils: Calcium Hydroxide is applied to acidic soils to neutralize acidity and improve soil quality, making it more conducive to plant growth.
- Water Bodies: It is used to neutralize acidic water bodies, such as lakes and rivers affected by acid rain, helping to restore ecological balance.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Calcium Hydroxide plays a role in carbon capture and storage technologies, where it reacts with carbon dioxide to form stable calcium carbonate. This process helps reduce CO₂ levels in the atmosphere, contributing to efforts to mitigate climate change.
Recent Research and Developments
The continuous exploration of Calcium Hydroxide’s properties and potential has led to significant advancements in its production methods, applications, and technologies. This section highlights recent innovations, emerging applications, and real-world examples that demonstrate the evolving landscape of Calcium Hydroxide usage.
Innovations in Production Methods
- Green Synthesis: Recent research has focused on developing environmentally friendly production methods for Calcium Hydroxide. Green synthesis techniques aim to minimize energy consumption and reduce carbon emissions during the production process. For example, utilizing solar energy to drive the hydration of calcium oxide is being explored to make the process more sustainable.
- Nanotechnology: The application of nanotechnology in the production of Calcium Hydroxide has led to the creation of nanoscale particles with improved reactivity and effectiveness. These nanoparticles offer superior performance in various applications, such as in water treatment and as additives in construction materials.
- Industrial By-products: Innovations in production methods include utilizing industrial by-products, such as waste gypsum from flue gas desulfurization processes, to produce high-purity Calcium Hydroxide. This not only provides a cost-effective raw material but also contributes to waste reduction and resource recycling.
Advanced Environmental Applications
- Water Purification: Research has led to the development of advanced water purification technologies that use Calcium Hydroxide to remove emerging contaminants, such as pharmaceuticals and endocrine-disrupting chemicals, from water supplies. These innovative applications help ensure safer drinking water.
- Soil Remediation: New technologies are employing Calcium Hydroxide for soil remediation, particularly in areas contaminated with heavy metals and other pollutants. By stabilizing these contaminants, Calcium Hydroxide helps restore soil health and prevent further environmental damage.
Safety and Handling
While Calcium Hydroxide offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to understand and adhere to proper safety measures when handling this compound. Here’s what you need to know to ensure safe usage:
Potential Health Hazards
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Direct contact with Calcium Hydroxide can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. Prolonged exposure may lead to burns and discomfort.
- Respiratory Issues: Inhaling Calcium Hydroxide dust or fumes can irritate the respiratory tract and may cause respiratory issues such as coughing or shortness of breath.
Recommended Safety Practices
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When working with Calcium Hydroxide, always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, safety goggles, and a respirator mask to protect against skin contact, eye irritation, and inhalation of dust or fumes.
- Proper Storage: Store Calcium Hydroxide in a dry, well-ventilated area away from incompatible substances. Keep containers tightly sealed to prevent moisture absorption and minimize the risk of accidental exposure.
First Aid Measures in Case of Exposure
- Skin Contact: In case of skin contact, immediately wash the affected area with plenty of water and mild soap. Remove contaminated clothing and seek medical attention if irritation persists.
- Eye Contact: If Calcium Hydroxide comes into contact with your eyes, flush them with water for at least 15 minutes, ensuring that eyelids are held open. Seek medical attention promptly.
- Inhalation: If you inhale Calcium Hydroxide dust or fumes and experience respiratory discomfort, move to a well-ventilated area and seek fresh air. If symptoms persist, seek medical attention.
In essence, this exploration of Calcium Hydroxide has not only deepened our understanding of its properties, uses, and safety measures but has also highlighted its pivotal role in shaping modern industry and fostering innovation. By harnessing its potential responsibly, we can continue to unlock new opportunities for growth, advancement, and sustainability in the years to come.
Annexe Chem Pvt Ltd. emerges as the optimal choice for Calcium Hydroxide manufacturing. Their commitment to delivering a qualitative range of fine chemicals, coupled with advanced technology for product packaging, ensures the integrity of the final product. With a state-of-the-art FDA-GMP facility and a robust distribution network, we offer quality products at competitive prices, guaranteeing timely delivery and customer satisfaction.

Akshita Patel
As an advocate for sustainability, Akshita is committed to driving positive change within the chemical industry. She actively seeks out environmentally friendly solutions and promotes the adoption of sustainable practices. Akshita believes that a balance between economic growth and ecological responsibility is crucial for the industry's long-term success. She is dedicated to finding innovative ways to minimize environmental impact while maximizing efficiency and profitability.
Related Blogs

- January 8, 2024
- By Akshita Patel
Calcium Carbonate: Your Go-to Guide
Calcium carbonate is a chemical composite with the formula CaCO3. It's a white powder or colorless.

- June 25, 2024
- By Akshita Patel
The Complete Guide to Sodium Chloride:.
Did you know that the average human body contains about 250 grams of sodium chloride, roughly.