What Is Calcium Gluconate? Uses, Benefits & Safety
Calcium Gluconate: More Than Just a Supplement—A Lifesaving Compound

- February 14, 2025
- By Akshita Patel
When you think of calcium, your mind probably jumps to strong bones and dairy products. But did you know that calcium plays a crucial role in keeping your heart beating and your muscles functioning properly? One of the most versatile forms of calcium—calcium gluconate—is not just a common supplement but a critical medical treatment used in emergency rooms and daily healthcare.
From treating calcium deficiencies to counteracting life-threatening conditions like hyperkalemia and cardiac arrest, calcium gluconate is far more than just another mineral supplement. In this blog, we’ll explore what makes calcium gluconate unique, how it works in the body, and why it’s an essential part of modern medicine.
What is Calcium Gluconate?
Calcium gluconate is a mineral supplement and medication used to treat calcium deficiencies and support various physiological functions. It is the calcium salt of gluconic acid, with the chemical formula C₁₂H₂₂CaO₁₄. Unlike other calcium compounds, calcium gluconate is more water-soluble, making it easier for the body to absorb and utilize.
How It Differs from Other Calcium Supplements
Calcium supplements come in various forms, but each has unique properties affecting its absorption, effectiveness, and use cases. Here’s how calcium gluconate compares:
Calcium Gluconate vs. Calcium Carbonate
- Calcium carbonate is widely used due to its high elemental calcium content (about 40%), but it requires stomach acid for proper absorption.
- Calcium gluconate, with only about 9% elemental calcium, is preferred for intravenous (IV) administration and medical treatments where quick calcium replenishment is needed.
Calcium Gluconate vs. Calcium Citrate
- Calcium citrate is better absorbed than calcium carbonate, especially for individuals with low stomach acid.
- Calcium gluconate is primarily used in hospital settings rather than for daily supplementation.
Because of its water solubility and bioavailability, calcium gluconate is preferred in medical treatments, particularly in cases requiring rapid calcium correction, such as hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, and certain heart conditions.
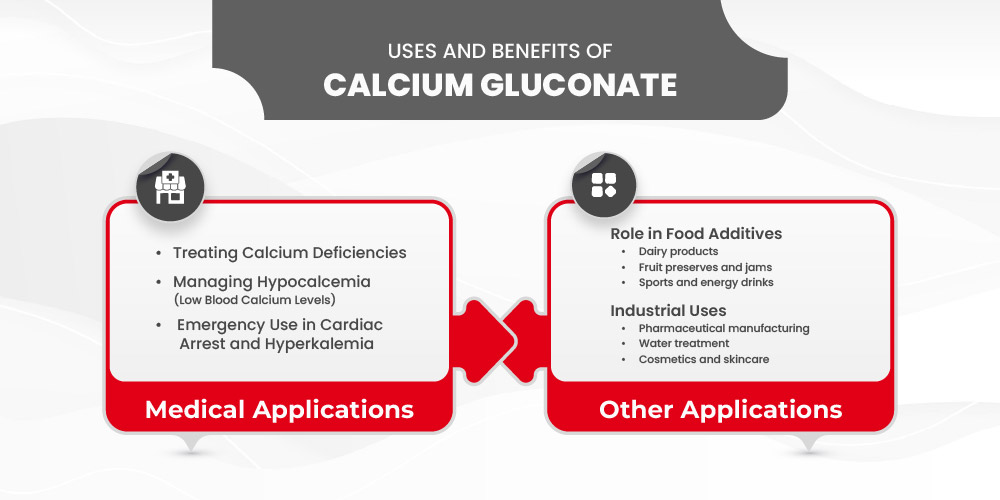
Uses and Benefits of Calcium Gluconate
Calcium gluconate is widely used in medicine, nutrition, and industry due to its role in maintaining calcium balance, supporting critical bodily functions, and acting as an additive in food and manufacturing processes. Below, we explore its key medical applications and other practical uses.
Medical Applications
1. Treating Calcium Deficiencies: Calcium is essential for bone strength, muscle contractions, nerve signaling, and blood clotting. When the body lacks sufficient calcium, it can lead to muscle cramps, brittle bones, and neurological issues.
Who needs it?
- People with osteoporosis or osteopenia
- Individuals with poor calcium absorption due to digestive disorders
- Patients recovering from long-term corticosteroid use, which can deplete calcium levels
How it helps:
- Calcium gluconate supplements restore calcium levels gradually.
- It is easier on the stomach than calcium carbonate, making it suitable for individuals with sensitive digestion.
2. Managing Hypocalcemia (Low Blood Calcium Levels): Hypocalcemia occurs when calcium levels in the blood drop too low, leading to muscle spasms, numbness, confusion, and even seizures. It can be caused by:
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Parathyroid gland disorders
- Chronic kidney disease
- Certain medications (e.g., diuretics, bisphosphonates)
How calcium gluconate helps:
- When taken orally, it helps gradually replenish calcium levels.
- In severe cases, intravenous (IV) calcium gluconate is administered in hospitals to quickly restore calcium and prevent life-threatening complications.
3. Emergency Use in Cardiac Arrest and Hyperkalemia
Cardiac Arrest: During a cardiac emergency, calcium gluconate is sometimes used to stabilize heart function. It helps in:
- Protecting the heart from dangerous arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats).
- Restoring calcium balance when deficiency contributes to cardiac complications.
Hyperkalemia (Excess Potassium in Blood): Hyperkalemia is a dangerous electrolyte imbalance where too much potassium accumulates in the bloodstream, potentially causing heart failure. How calcium gluconate helps:
- It protects the heart muscles from the effects of high potassium levels.
- It does not lower potassium directly but acts as a temporary stabilizer, preventing immediate cardiac risks while other treatments work to remove excess potassium.
Other Applications
1. Role in Food Additives: Calcium gluconate is widely used in the food industry as a calcium fortifier and stabilizer. It appears in:
- Dairy products – Enhances calcium content in milk and yogurt.
- Fruit preserves and jams – Acts as a firming agent to maintain texture.
- Sports and energy drinks – Provides an easy-to-absorb calcium source.
It is favored because it is mild in taste, highly soluble, and easily digestible compared to other calcium additives.
2. Industrial Uses: Beyond nutrition and medicine, calcium gluconate has applications in various industries:
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing – Used in tablets, syrups, and injections as a source of calcium.
- Water treatment – Helps in removing fluoride toxicity in contaminated water.
- Cosmetics and skincare – Occasionally added to lotions and anti-aging creams due to its role in skin cell renewal.
From medical emergencies to food preservation, calcium gluconate plays an important role in healthcare and everyday products. Whether it’s replenishing calcium levels, protecting heart function, or enhancing food quality, this compound continues to be an essential part of modern life.
Dosage and Administration of Calcium Gluconate
Calcium gluconate is available in multiple forms and is used to treat a variety of conditions. The dosage and administration method depends on the severity of the calcium deficiency or medical condition. Below is a breakdown of its recommended use, administration methods, and safety precautions.
Recommended Dosage for Different Conditions
The appropriate dosage varies based on age, health status, and whether the treatment is for a mild calcium deficiency or a critical condition like hypocalcemia.
For Calcium Deficiency (Oral Supplementation)
- Adults: 500 mg to 2 g per day, divided into smaller doses.
- Children: Dosage is determined based on weight and doctor recommendations.
For Hypocalcemia (Low Blood Calcium – IV Administration)
- Mild cases: 1-2 g of calcium gluconate diluted in saline over 1-2 hours.
- Severe cases: A slow IV infusion of 10% calcium gluconate, carefully monitored to prevent cardiac complications.
For Hyperkalemia (High Potassium Levels – IV Administration)
- A 10 mL dose of 10% calcium gluconate administered over 5-10 minutes to stabilize heart function.
For Cardiac Arrest (IV Emergency Use)
- 10-20 mL of 10% calcium gluconate, administered slowly under close supervision.
Methods of Administration
Calcium gluconate can be taken in different ways depending on the condition being treated:
- Oral (Tablets or Liquid): Used for daily calcium supplementation. Should be taken with food to improve absorption.
- Intravenous (IV): Used in hospitals for critical conditions like hypocalcemia and cardiac complications. Must be administered slowly to avoid side effects.
- Topical (Ointments or Gels): Used to treat hydrofluoric acid burns in chemical exposure cases.
Precautions and Safety Guidelines For Using Calcium Gluconate
- Monitor Blood Calcium Levels: Overuse can lead to hypercalcemia (excess calcium in the blood), causing kidney and heart issues.
- Avoid Rapid IV Injection: Must be given slowly to prevent cardiac arrhythmias or sudden drops in blood pressure.
- Drug Interactions: Calcium gluconate may interfere with certain medications, including beta-blockers, tetracycline antibiotics, and bisphosphonates.
- Kidney Patients Should Use Caution: Those with kidney disease should take calcium supplements only under medical supervision to avoid calcium buildup in the body.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Using Calcium Gluconate
While calcium gluconate is generally safe when used correctly, it may cause side effects ranging from mild digestive issues to serious complications in high doses or improper administration.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Nausea, constipation, bloating.
- Injection Site Reactions (IV Use): Pain, redness, or irritation at the injection site.
- Mild Drop in Blood Pressure: Can cause dizziness or lightheadedness.
Serious Risks and Complications
- Hypercalcemia (Excess Calcium in Blood):
- Symptoms: Fatigue, excessive thirst, kidney stones, confusion, irregular heartbeat.
- Solution: Lower calcium intake and increase hydration; severe cases may require medical intervention.
- Cardiac Risks (With IV Use):
- Rapid IV infusion can cause arrhythmias, bradycardia (slow heartbeat), or cardiac arrest.
- Always administer under medical supervision.
- Calcium Overdose:
- Can lead to calcium deposits in arteries or kidneys, increasing the risk of kidney stones and organ damage.
- Treatment may involve IV fluids and diuretics to flush out excess calcium.
Who Should Avoid Calcium Gluconate?
- Individuals with hypercalcemia or severe kidney disease.
- Patients taking digoxin (a heart medication), as calcium gluconate can worsen toxicity.
- Those with parathyroid disorders, unless prescribed by a doctor.
- People with calcium-sensitive conditions, such as sarcoidosis, should consult a physician before use.
Calcium gluconate is a vital supplement and medical treatment, but it must be used with caution. Whether taken orally, intravenously, or topically, proper dosage, administration, and monitoring are crucial to prevent complications. Always consult a healthcare professional before using calcium gluconate, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking other medications. Calcium gluconate is more than just a supplement—it plays a crucial role in treating calcium deficiencies, managing critical health conditions like hypocalcemia and hyperkalemia, and even supporting industrial and food applications. Whether used as a daily supplement or a life-saving medical treatment, its effectiveness depends on proper dosage and administration. However, like any supplement or medication, it must be used with caution, under medical supervision when necessary, to avoid potential side effects and risks.When it comes to sourcing high-quality calcium gluconate, Annexe Chem stands out as the leading calcium gluconate manufacturer in India. With a commitment to quality, purity, and innovation, Annexe Chem ensures that every batch meets stringent industry standards. Whether you need calcium gluconate for pharmaceutical, food, or industrial applications, you can trust Annexe Chem for reliable, high-grade solutions tailored to your needs.
For more information on calcium gluconate or to explore our product range, get in touch with Annexe Chem today!

Akshita Patel
As an advocate for sustainability, Akshita is committed to driving positive change within the chemical industry. She actively seeks out environmentally friendly solutions and promotes the adoption of sustainable practices. Akshita believes that a balance between economic growth and ecological responsibility is crucial for the industry's long-term success. She is dedicated to finding innovative ways to minimize environmental impact while maximizing efficiency and profitability.
Related Blogs

- April 15, 2025
- By Akshita Patel
The Ultimate Guide to Di Sodium.
Ever wondered what keeps your favorite soft drinks fizzy, your cheese perfectly creamy, or even helps.

- August 6, 2024
- By Akshita Patel
Everything You Need to Know About.
In the vast world of industrial and scientific materials, Calcium Sulphate Anhydrous often flies under the.